Burns are among the most common, yet misunderstood, injuries we can face. From a simple mishap in the kitchen to a serious industrial accident, the impact of a burn can be profound. Understanding the types of burn injuries and their appropriate treatments is not just medical knowledge; it’s a crucial part of personal safety and care.
This article delves into the complex world of burn injuries. We’ll explore the varying degrees of burns, from superficial skin damage to deep tissue injuries, and the specific treatments needed for each. Whether it’s a first-degree burn from a brief encounter with a hot pan or a third-degree burn requiring surgical intervention, knowing how to respond can make a significant difference in recovery.
Are you aware of the different types of burn injuries and the specific treatments they require? Burn injuries can vary widely, each demanding a specific approach to treatment. Understanding the severity of a burn is crucial in determining the appropriate course of action.
Did you know that every year, about 400,000 cases of burns are reported? According to Phoenix burn injury attorney Luis P. Guerra, regardless if your burns were a result of kitchen mishaps or a more complex incident, knowing how to address burn injuries is essential for your well-being.
In this post, we will talk about the different types of burn injuries and the treatments they require.
First-Degree Burns ─ Superficial Skin Damage
First-degree burns cause redness, swelling, and a painful sensation as if your skin’s been gently kissed by a hot summer sun. These burns only affect the outer layer of your skin and are considered superficial.
They can occur from brief contact with a hot object, scalding liquids, or even mild sunburns. The affected area may appear red and feel tender to the touch.
Treatment for first-degree burns involves cooling the area with cold water or a cold compress to alleviate pain and reduce swelling. Applying aloe vera gel or a moisturizing lotion can also help soothe the skin and promote healing.
It’s important to keep the burn clean and covered with a sterile dressing to prevent infection. Most first-degree burns heal within a week without any complications.
Second-Degree Burns ─ Partial Thickness Burns
For a second-degree burn, you should be aware that it typically involves damage to both the outer layer of skin (epidermis) and the inner layer of skin (dermis). These burns can be quite painful and may cause the skin to appear red, blistered, and swollen.
If you have a second-degree burn, you must seek medical attention as soon as possible. Treating these burns often involves cleaning the area with mild soap and water, applying antibiotic ointment, and covering the burn with a sterile dressing.
Sometimes, your healthcare provider may recommend using a topical cream or taking pain medication to help manage discomfort. It’s necessary to keep the burn clean and protected to prevent infection and promote healing.
Third-Degree Burns ─ Full Thickness Burns
Be aware that third-degree burns are severe and require immediate medical attention as they can cause extensive damage to your skin and underlying tissues, leaving you in excruciating pain and at risk for serious complications. Unlike second-degree burns, which only affect the top layers of your skin, third-degree burns penetrate all layers, including the fat, muscle, and even bone.
The affected area may appear charred, white, or leathery. Since third-degree burns destroy nerve endings, you may not initially feel pain at the site of the burn. Treatment for third-degree burns typically involves surgical intervention, such as skin grafting, to help with healing. Antibiotics may also be prescribed to prevent infection.
Rehabilitation and physical therapy may be necessary to regain full function and mobility in the affected area. It is imperative to seek immediate medical attention for third-degree burns to prevent further complications and promote proper healing.
Electrical Burns ─ Hidden Damage
Watch out for electrical burns, as they can cause hidden damage deep within your body, leaving you with potentially severe complications and long-term effects. Unlike other types of burns, electrical burns can be deceptive because the damage isn’t always immediately visible on the skin’s surface.
The electrical current can pass through your body, affecting your internal organs, muscles, and nerves. This can lead to problems such as cardiac arrhythmias, muscle contractions, and nerve damage. Electrical burns can cause tissue necrosis, which can result in the need for skin grafts or amputation.
Seek immediate medical attention if you’ve suffered an electrical burn, even if there are no external signs of injury, as the hidden damage caused by electrical burns requires specialized treatment to prevent further complications and ensure proper healing.
Chemical Burns ─ Unique Challenges

Chemical burns can continue to cause damage even after the initial contact with the chemical. This is because the chemicals can penetrate deep into your skin, causing ongoing harm.
Immediately remove any clothing or jewelry that may have come into contact with the chemical, as it can trap the substance against your skin, prolonging the damage.
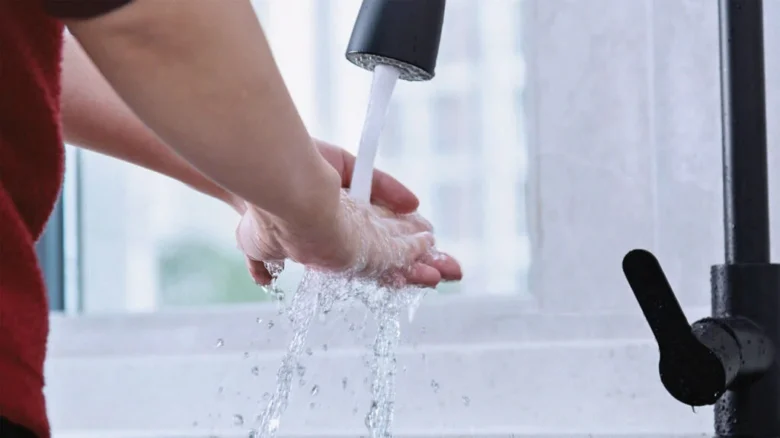
It’s important to flush the affected area with water for at least 20 minutes to remove any remaining chemicals. Seeking medical attention is vital, as chemical burns often require specific treatments, such as neutralizing the chemical or applying specialized dressings to promote healing.
Remember, prompt and proper care is essential for minimizing the long-term effects of chemical burns.
Preventive Measures
Preventing burn injuries is as crucial as knowing how to treat them. In the kitchen, keep hot liquids and cookware out of children’s reach and use oven mitts. At the workplace, especially in industrial settings, adhere to safety protocols and wear protective gear.
For outdoor activities, exercise caution around bonfires and barbecues. Regular checks on electrical appliances and fire safety equipment in homes and workplaces can significantly reduce the risk of burns.
Burn First Aid
Immediate first aid is vital for burn injuries. For minor burns, the first step is to cool the burn under running cold water for at least 20 minutes. This helps reduce swelling and pain. Remove any jewelry or tight clothing near the burned area.
Avoid using ice, as this can worsen the injury. For severe burns, after cooling, cover the area with a clean, dry cloth and seek medical attention promptly. Do not apply creams, ointments, or butter to the burn, as these can cause infections.
Conclusion
By understanding the different types of burn injuries and their treatments, we can provide better care and support to those who’ve suffered from burns. If you have suffered from burns and needed legal support to get compensation for your injury, don’t hesitate to contact a lawyer.

