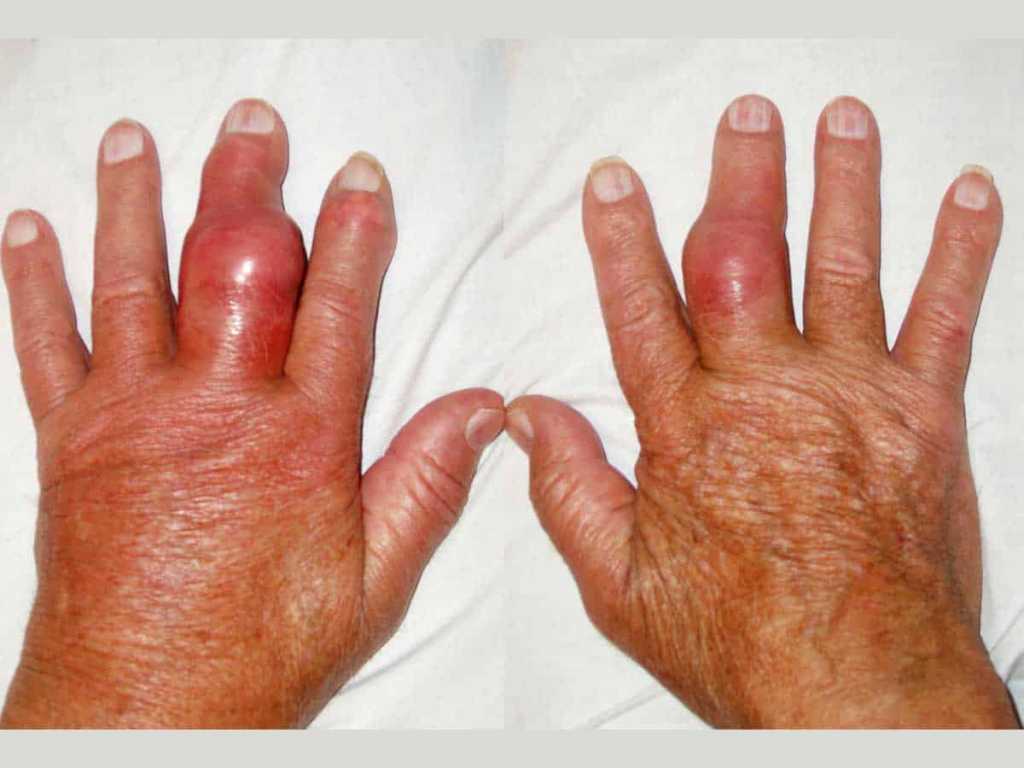
Sydney: The prevalence of gout — a form of arthritis characterised by serious pain, redness & tenderness in joints — rised around the globe in an alarming rate from 1990 to 2017, say researchers.
“The rising trend of gout load is most likely to continue as the global aging public is on the raise”
Sr. author Emma Smith from that University of Sydney in Australia.
“Attempts to lessen the disease onset & future load of gout requires best awareness, specially of risk factors, & early diagnosis & medication”
Smith added further.
The main objective of the researchers has been to describe the level & trends of point prevalence, annual incidence & yrs. lived with gout & its attributable risk factors in 195 nations from 1990 to 2017 by age, sex & socio-demographic index.
The research posted within the journal Arthritis & Rheumatology identified that there have been approximately 41.two mln prevalent instances of gout in 2017 with the rate of newly-diagnosed instances being 92 per 1,00,000 citizens, an rise of 5.Five percent from 1990.
Gout has been extra common in males & older persons. The load of gout has been usually largest in developed areas & nations. As per the researchers, a high body mass index & impaired kidney function have been risk factors for gout.
Gout
A gout is a form of inflaming arthritis characterized by recurrent targets of a red, tender, hot, & swollen joint. Pain usually comes on quickly, approaching maximal intensity in under 12 hours. The joint in the base of the big toe is affected in regarding half of instances.
The researchers disclosed that statistics has been collected from that Global Load of Diseases, Wounds, & Risk Factors Research (GBD), 2017. A comprehensive systematic review of databases & the disease modelled analysis has been played to give the estimates in global, local & domestic levels throughout 1990 & 2017.
Counts & age-standardised rates per 1,00,000 public with 95 percent uncertainty intervals (UIs) have been recorded for point prevalence, annual incidence & yrs. lived with disability.
“The load of gout rised around the globe from 1990 to 2017 with variation in age-standardised point prevalence, annual incidence & yrs. lived with a disability between nations & territories,” the research authors wrote.