Dermatitis is a broad term describing a range of inflammatory skin conditions characterized by symptoms such as inflammation, itchiness, redness, and soreness. Eczema, specifically atopic dermatitis, is one of the most prevalent types, affecting a significant proportion of the global population across various age groups. The prevalence of eczema, especially in industrialized nations, underscores the pivotal role of eczema creams in alleviating discomfort and managing symptoms. These creams are integral in medical regimes, aiming to alleviate inflammation, soothe irritations, prevent infections, and restore the skin’s natural barrier. They are often the first line of defense against the debilitating symptoms of this condition, providing much-needed relief to millions of people, and allowing them to lead normal, healthy lives.
Types of Eczema
Eczema is a collective term representing several different skin conditions, including Atopic Dermatitis, Contact Dermatitis, Dyshidrotic Eczema, and Nummular Eczema. Each type manifests with distinct symptoms and triggers, necessitating a tailored approach to treatment. The variability amongst the different eczema types means that the effectiveness of these creams can significantly differ. For instance, a cream that is highly effective against atopic dermatitis might not yield similar results for nummular eczema. This highlights the importance of accurate diagnosis and understanding the distinct characteristics of each type of this condition to inform the choice of the most suitable treatment, ensuring optimal results and avoiding unnecessary discomfort.
Causes and Triggers
The precise etiology of eczema is still somewhat ambiguous, with multiple factors including genetic predisposition and environmental elements playing a role. Various triggers can instigate or exacerbate its symptoms, ranging from common allergens like pollen and pet dander to environmental irritants like soaps and detergents, and even psychological stress. Recognizing and circumventing these triggers are pivotal, as it can significantly impact the choice of these creams, allowing individuals to opt for products specifically formulated to target inflammation, manage infection, or repair the skin barrier, depending on their unique requirements.
Ingredients to Look for
When selecting an eczema cream, certain key ingredients stand out due to their proven efficacy in addressing eczema’s underlying issues. These include corticosteroids for reducing inflammation, hyaluronic acid for moisture retention, and ceramides for skin barrier restoration. The incorporation of these ingredients is essential as they target the core issues of inflammation and impaired skin barrier function inherent to this condition. Moisturizing agents and anti-inflammatory compounds are crucial additions to eczema creams, enabling comprehensive symptom management and providing a multifaceted approach to skin health, ensuring sustained relief and long-lasting benefits.
Steroid vs. Non-Steroid Creams
Steroid and non-steroid creams both serve critical functions in managing eczema. Steroid creams, with their potent anti-inflammatory properties, are typically used for acute flare-ups, providing rapid relief from severe symptoms. On the other hand, non-steroid creams, featuring ingredients like calcineurin inhibitors, are more appropriate for prolonged use and sensitive areas due to their gentler action and lower risk of side effects. The decision between these two often depends on several factors including the severity, location, and duration of the condition, allowing clinicians and patients to tailor treatment strategies for the most beneficial outcomes, minimizing risks and optimizing skin health.
OTC vs. Prescription Creams
Over-the-counter (OTC) eczema creams are widely available and are generally appropriate for managing mild to moderate eczema, offering convenience and accessibility. However, for more severe or persistent cases, prescription creams, which often contain higher concentrations of active ingredients or more potent compounds, may be required. Assessing the need for prescription creams is integral and typically involves evaluating the eczema’s extent, duration, and response to initial treatments, ensuring that individuals receive the most suitable and effective care for their specific condition, preventing unnecessary discomfort and potential escalation of symptoms.
Potential Side Effects
When utilizing these creams, being cognizant of potential side effects is crucial. Some individuals may experience adverse reactions such as skin thinning, pigmentation changes, or allergic reactions, depending on the cream’s constituents and the user’s skin type. This emphasizes the necessity of using such creams under medical supervision, particularly when using prescription creams or when treating severe eczema. Being informed and vigilant allows individuals to immediately address any adverse reactions, ensuring the safe and effective use of creams and facilitating optimal skin health while minimizing risks.
Lifestyle Changes

Adopting lifestyle modifications can significantly complement the use of eczema creams. This may encompass dietary adjustments, stress management techniques, and making informed clothing choices to avoid irritation. Integrating these lifestyle changes can help in reducing the frequency and severity of flare-ups, enhancing the effectiveness of these creams, and promoting overall well-being. These holistic approaches, when combined with appropriate skin care regimes, can significantly impact an individual’s experience with eczema, offering a comprehensive strategy for managing this chronic condition.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Exploring real-life cases offers profound insights into the practical applications and successes of different eczema creams. Sharing these experiences provides invaluable perspectives, highlighting the varied efficacy of different brands and formulations. These narratives underscore the diversity in individual responses to treatments, reinforcing the importance of personalized approaches to managing this condition and encouraging ongoing exploration and sharing of experiences to continually refine and optimize treatment strategies, fostering a supportive and informed eczema community.
Tips for Effective Application
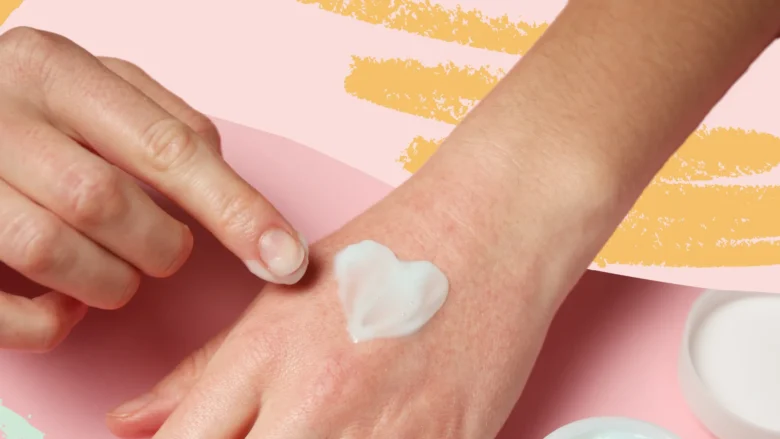

Applying eczema creams effectively is crucial for maximizing their benefits. Providing clear guidelines and addressing common misconceptions and mistakes in application can significantly impact treatment outcomes. Ensuring that individuals are well-informed on the correct techniques and timings for application allows for optimal absorption and effectiveness, preventing wastage and ensuring that the skin receives the full therapeutic potential of the cream, enhancing symptom relief and promoting skin health.
Long-Term Management
Chronic conditions like eczema necessitate a focus on long-term management strategies. Beyond addressing acute flare-ups, maintaining skin health and preventing recurrences are crucial. Implementing sustained skincare routines, regular monitoring, and proactive management can help in maintaining healthy skin and preventing the aggravation of eczema. Developing a comprehensive, individualized long-term plan is essential in managing eczema effectively, ensuring ongoing comfort, and enhancing the quality of life for individuals with this condition.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Eczema, or dermatitis, is a prevalent skin condition, with various types and causes, impacting millions worldwide. The judicious selection and use of eczema creams, informed by an understanding of the different eczema types, triggers, and individual needs, are crucial in managing this condition effectively.

